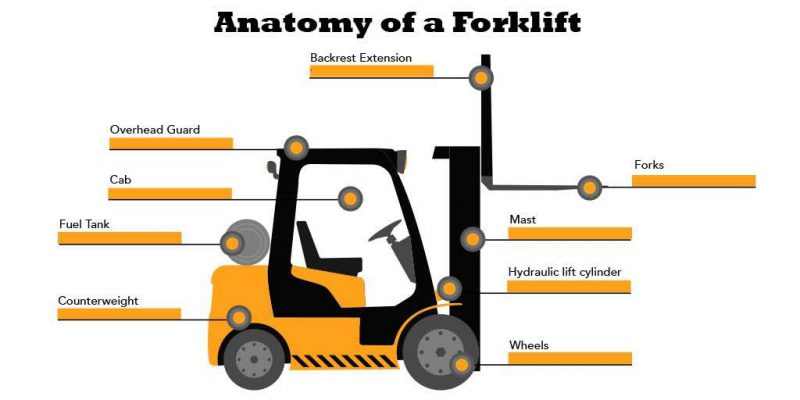
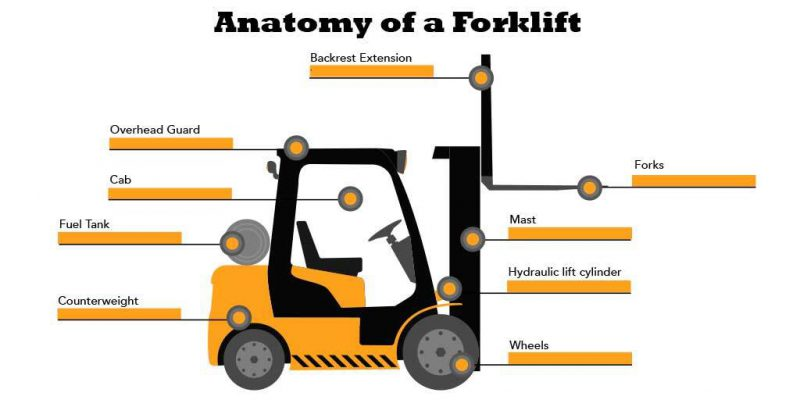
Cab
The cab is where the operator sits or stands and contains the controls for operating for the forklift. The controls include the steering wheel, lift controls, brake and accelerator pedals, safety signals, and more.
Overhead Guard
Directly above the cab is the overhead guard. This protects the forklift operator from weather conditions, and falling materials.
Counterweight
Essential to the safe functioning of a counterbalance forklift truck, the counterweight prevents trucks from tipping over when lifting and transporting a heavy load.
Forks
The forks are two large, steel tines which jut out from the truck and are designed to handle cargo and materials, lift pallets, and bring product down from high shelves.
Undercarriage
The undercarriage of a forklift is the underside of the cab and contains the mechanics of the truck. Like an automobile, the undercarriage of the forklift should be inspected and maintained regularly for safety and longevity.
Fuel Tank
Gas-powered forklifts have a fuel tank attached to the rear which holds the fuel for the truck. Depending on the model, these fuel tanks may contain gasoline, diesel, LPG, or CNG.
Wheels
The type of tires found on a forklift is dependent upon the conditions it is being used in.
· Cushion tires, designed for indoor, paved surfaces, are composed of solid rubber and are directly pressed onto the wheel.
· Solid pneumatic tires are designed of solid rubber and practically indestructible. They are used for indoor and outdoor applications.
· Air-filled pneumatic tires have a deep tread and are made of strong, long-lasting rubber material. These tires are better for rough, outdoor terrain.
Mast
The forks move up and down on the mast on a lift truck.
Hydraulic Lift Cylinder
Needed to move the forks up the mast, the hydraulic lift cylinder is responsible for the total vertical lift of the reach truck.